Absolute value in Excel is one of the most essential mathematical functions that every spreadsheet user should master.
Whether you’re a beginner just starting with Excel or a professional looking to enhance your data analysis skills, understanding how to work with absolute value in Excel will significantly improve your ability to handle numerical data effectively.
The concept of absolute value in Excel becomes particularly important when you need to calculate distances, differences, or when working with financial data where negative values need to be converted to positive ones.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about using absolute value in Excel, from basic functions to advanced applications.
Table of Contents
What is Absolute Value and Why Does It Matter?
Before we look at how Excel uses it, it’s important to first understand the basic concept of absolute value.
In math, the absolute value represents how far a number is from zero on the number line, without considering whether it is positive or negative.
This means that both -5 and +5 have an absolute value of 5.
In Excel, the ABS function is widely used for handling real-world data scenarios.
You might need to calculate the absolute difference between two values, find the magnitude of variations in your data, or convert negative numbers to positive ones for specific calculations.
Understanding absolute value in Excel is crucial for tasks like financial modeling, statistical analysis, and data cleaning.
When working with spreadsheets, you’ll often encounter situations where negative values can skew your analysis.
For example, if you’re calculating the average deviation from a mean, negative and positive deviations might cancel each other out, giving you misleading results. This is where absolute value in Excel becomes invaluable.
The ABS Function: Your Go-To Tool
The primary way to calculate absolute value in Excel is through the ABS function. This built-in function is straightforward to use and incredibly powerful for various applications.
The syntax for the ABS function is simple:
=ABS(number)Where “number” can be:
- A direct numerical value
- A cell reference
- A formula that returns a numerical result
Let’s look at some practical examples. If you have the value -15 in cell A1, you can calculate its absolute value by typing:
=ABS(A1)The result will be 15, which is the positive version of -15.
The true advantage of using absolute value in Excel comes from how versatile it is. You can combine the ABS function with other mathematical operations to create more complex formulas. For instance, if you want to find the absolute difference between two cells:
=ABS(A1-B1)This formula calculates the absolute value of the difference between cells A1 and B1, ensuring you always get a positive result regardless of which value is larger.
Common Applications and Use Cases
Understanding when and how to apply absolute value in real-world scenarios is crucial for maximizing its utility. Here are some common applications:
Financial Analysis
In financial modeling, absolute value helps calculate absolute returns, deviations from budgets, and variance analysis. When comparing actual expenses to budgeted amounts, you often want to know the magnitude of the difference without caring about the direction.
Statistical Calculations
When performing statistical analysis, absolute value is essential for calculating mean absolute deviation, which provides insights into data variability.
Unlike standard deviation, mean absolute deviation gives equal weight to all deviations from the mean.
Data Cleaning and Validation
During data cleaning processes, absolute value in Excel helps identify outliers and inconsistencies in your datasets.
You can use it to flag data points that deviate significantly from expected ranges.
Advanced Techniques and Combinations
While the basic ABS function covers most needs, combining absolute value in Excel with other functions creates powerful analytical tools.
Using ABS with IF Statements
You can combine absolute value in Excel with conditional logic to create sophisticated formulas:
=IF(ABS(A1-B1)>10,"Significant Difference","Minor Difference")This formula checks if the absolute difference between two cells exceeds 10 and returns appropriate text.
Array Formulas with Absolute Values
For more advanced users, absolute value in Excel can be incorporated into array formulas for complex calculations across multiple cells simultaneously.
Combining with SUMPRODUCT
When you need to sum absolute values across a range, combining absolute value in Excel with SUMPRODUCT creates elegant solutions:
=SUMPRODUCT(ABS(A1:A10))Practical Examples and Step-by-Step Tutorials
We’ll explore some practical cases to see how absolute value can be effectively applied in Excel.
Example 1: Budget Variance Analysis
Imagine you’re analyzing monthly budget variances for different departments. Column A contains your budgeted amounts, while Column B shows the actual expenses. To calculate absolute variances:
=ABS(B2-A2)This gives you the magnitude of each variance, regardless of whether departments overspent or underspent.
Example 2: Performance Tracking
For performance tracking, you might want to measure how far individual scores deviate from a target. If your target is in cell C1 and individual scores are in column D:
=ABS(D2-$C$1)The dollar signs create an absolute reference to the target, allowing you to copy the formula down the column.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting
Even experienced users sometimes encounter issues when working with absolute value in Excel. Here are common mistakes and their solutions:
Mistake 1: Forgetting Cell References
Always ensure your cell references are correct when using absolute value in Excel. A common error is referencing empty cells, which returns 0.
Mistake 2: Mixing Data Types
The ABS function works with numerical data. If you’re working with text that looks like numbers, you might need to convert it first using the VALUE function.
Mistake 3: Circular References
When creating complex formulas involving absolute value in Excel, be careful not to create circular references where a cell references itself directly or indirectly.
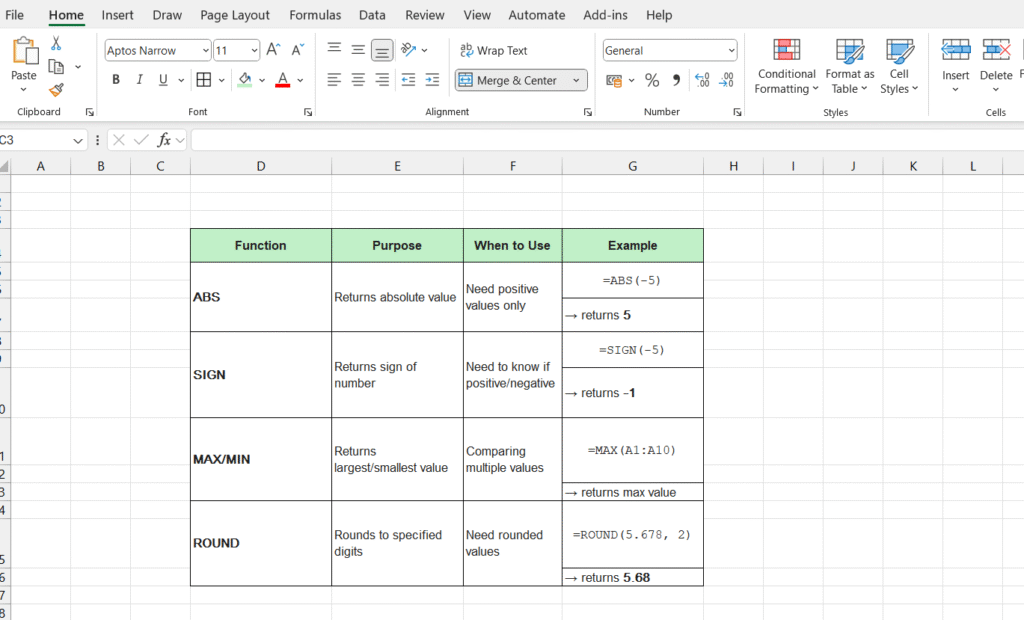
Comparison Table: ABS vs Other Functions
Here’s a helpful comparison of when to use absolute value in Excel versus other similar functions:
| Function | Purpose | When to Use | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABS | Returns absolute value | Need positive values only | |
| SIGN | Returns sign of number | Need to know if positive/negative | |
| MAX/MIN | Returns largest/smallest value | Comparing multiple values | |
| ROUND | Rounds to specified digits | Need rounded values | |
Best Practices for Using Absolute Value
To maximize the effectiveness of absolute value in Excel in your spreadsheets, follow these best practices:
Consistency in Application
When using absolute value in Excel across multiple calculations, ensure consistent application. If you’re analyzing variances, apply absolute value consistently to all related calculations.
Documentation and Comments
Document your use of absolute value in Excel functions, especially in complex spreadsheets. This helps others (and future you) understand the logic behind your calculations.
Error Handling
Consider incorporating error handling when using absolute value in Excel in complex formulas. The IFERROR function can help manage unexpected results.
Performance Considerations
While absolute value in Excel calculations are generally fast, in very large datasets, consider the performance impact of complex array formulas involving ABS functions.
For additional Excel tips and advanced techniques, you can explore more resources at www.techtellent.com, which offers comprehensive tutorials on spreadsheet optimization and data analysis.
Integration with Other Excel Features
The power of absolute value in Excel becomes even more apparent when integrated with other Excel features like pivot tables, charts, and conditional formatting.
Conditional Formatting with Absolute Values
You can use absolute value in Excel within conditional formatting rules to highlight cells based on the magnitude of their values, regardless of sign.
Pivot Table Applications
In pivot tables, absolute value in Excel can help create summary statistics that focus on magnitude rather than direction of changes.
Charting and Visualization
When creating charts, absolute value in Excel ensures that negative values don’t create misleading visual representations, particularly in bar charts and trend analyses.
Microsoft’s official documentation provides additional insights into advanced Excel functions and their applications, which you can find on their official support page.
Related Excel Resources and Advanced Learning
Now that you’ve mastered the index match formula, you can apply this knowledge to various Excel projects and templates.
Understanding lookup functions becomes especially valuable when working with complex business scenarios and automated reporting systems.
If you’re just starting your Excel journey, our comprehensive Excel for Beginners PDF guide provides foundational knowledge that complements the index match formula techniques covered here. This resource helps you build the groundwork necessary for advanced formula applications.
For project management applications, the index match formula works exceptionally well with structured templates like our Google Sheets Product Roadmap Template. While designed for Google Sheets, the lookup principles transfer perfectly to Excel environments where you need dynamic data retrieval for project tracking.
Financial professionals will find the index match formula particularly useful when working with our specialized templates. The Debt Service Coverage Ratio Formula in Excel guide demonstrates how lookup functions integrate with financial calculations. Similarly, our Profit Margin Formula Excel Guide shows practical applications of the index match formula in financial analysis scenarios.
Business process optimization benefits greatly from the index match formula’s flexibility. Our RFI Template Excel guide showcases how lookup functions streamline vendor management and procurement processes. The same principles apply to customer relationship management in our Real Estate CRM Excel Template, where the index match formula enables quick client information retrieval.
Reporting automation represents another powerful application area. Our Monthly Sales Report Template in Excel leverages lookup functions similar to the index match formula for dynamic report generation. For debt management scenarios, the Debt Schedule Template Excel demonstrates how lookup functions create flexible payment tracking systems.
Advanced Excel users should explore our guide on how to Automate Excel Reports using best practices, which shows how the index match formula integrates with other automation techniques. Additionally, our Pivot Table Practice Exercises complement lookup function skills by teaching another essential data analysis method.
These resources work together to create a comprehensive Excel skill set where the index match formula serves as a fundamental building block for more complex data manipulation and analysis tasks.
Conclusion
Mastering absolute value in Excel opens up numerous possibilities for data analysis and mathematical calculations.
From basic variance analysis to complex statistical computations, absolute value in Excel serves as a fundamental building block for many advanced spreadsheet applications.
The key to effectively using absolute value in Excel lies in understanding not just the syntax, but the practical applications and best practices that make your spreadsheets more accurate and insightful.
Whether you’re working with financial data, conducting statistical analysis, or simply cleaning up datasets, absolute value in Excel will prove to be an invaluable tool in your spreadsheet arsenal.
Remember that absolute value in Excel is just one of many powerful functions available in the platform.
As you continue to develop your Excel skills, consider how absolute value in Excel can be combined with other functions to create even more sophisticated analytical tools.
Practice with different scenarios and datasets to fully appreciate the versatility and power of absolute value in Excel.
By incorporating absolute value in Excel into your regular workflow, you’ll find that many complex data analysis tasks become more manageable and your results more reliable.
The investment in learning this fundamental function will pay dividends in improved spreadsheet accuracy and analytical capability.
